How is Augmented Reality used in industries?

Let’s see what recent research looking into Industrial Augmented Reality says!
We have written about applying smart glasses into the warehouse picking process, and with that presented our vision picking solution, Readii. But there are many more industry sectors where others have investigated how to apply AR and what gains and pitfalls there are, so let’s take a look and see what we can learn about AR in other settings than warehouses.
A systematic literature review
A group of scientists has tried to answer five questions regarding industrial AR through a systematic literature review covering articles, reviews, and patents ranging from 2012 to 2018. The questions they have looked into are:
- What is the primary purpose of AR in industrial environments?
- Which kind of industry has developed AR for their production process?
- How AR applications have been developed for production environments?
- Which are the leading technology benefits?
- Which are the main challenges to apply AR in production environments?
Primary purpose
The researchers identified ten areas of usage for AR applications; manual assembly, maintenance, process monitoring, training, process simulation, quality inspection, picking process, operational setup, ergonomics and safety and, robot programming and operations.
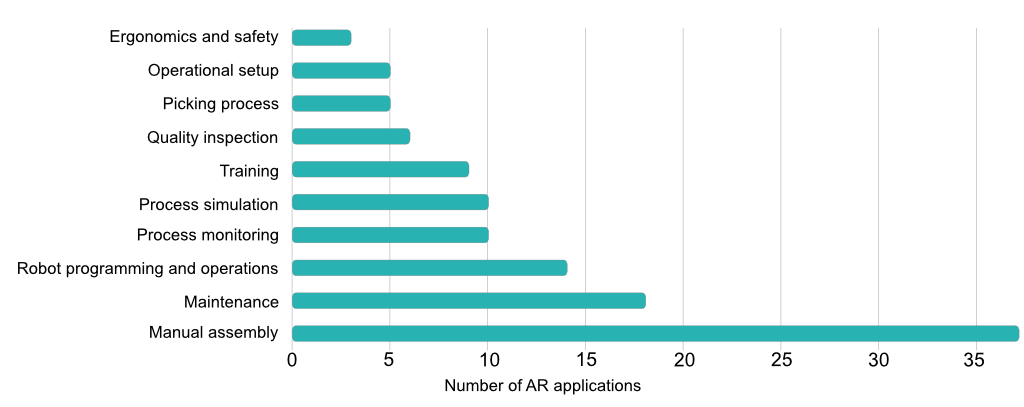 Disribution of AR applications in relation to purpose
Disribution of AR applications in relation to purpose
They also found several combinations of the above, with the most common ones being picking process and manual assembly or operational setup, and manual assembly with simultaneous quality inspection.
Some examples of the above areas can be found in remote assistance and of course our own vision picking solution.
Industries using AR
Several industrial segments where AR applications have been developed were found, these were architecture, engineering, aeronautics, energy, government, logistics, marine, mechanical, electronics/automation, automotive, and construction and facilities management (AEC/FM). When combined with the purpose of the AR application the distribution looks like below.
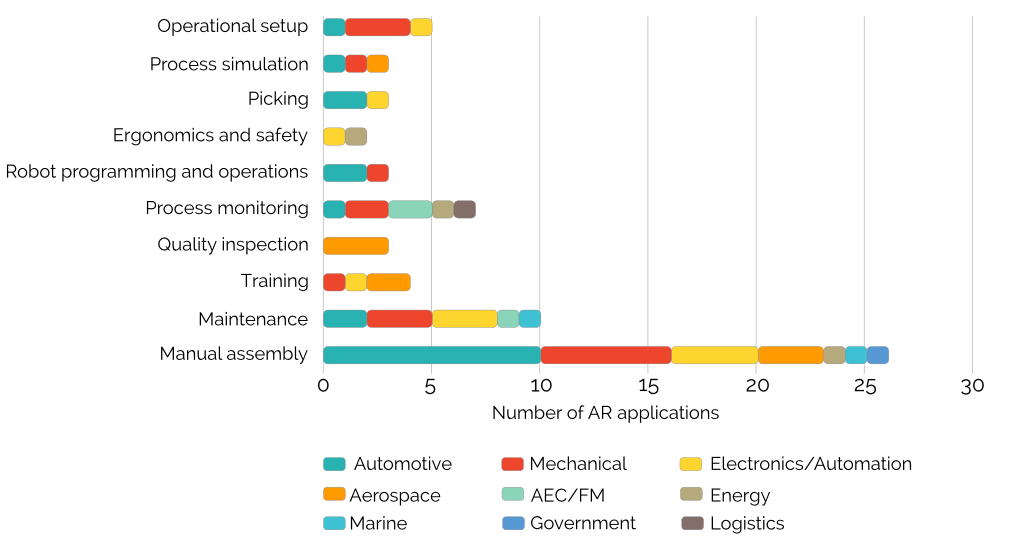 Disribution of AR applications in relation to industrial segment and purpose
Disribution of AR applications in relation to industrial segment and purpose
The segments above represented 52% of the AR solutions, the remaining 48% were classified as general since they were not developed for any explicit segment. Based on this the authors concluded that industries are more interested in finding general applications applicable for adaption to their business scenario than to develop single-purpose applications to solve their problems.
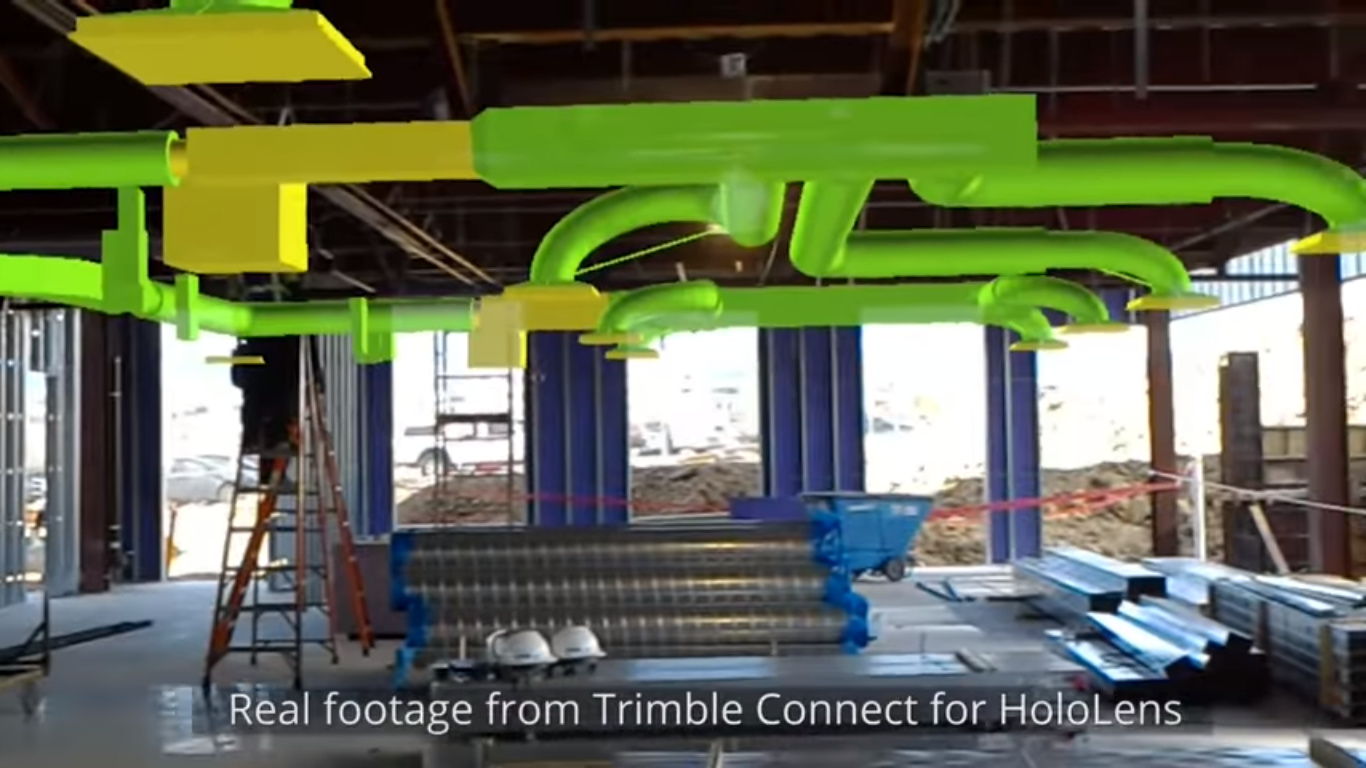 Trimble enables holographic elements to be presented in the real world, here in construction
Trimble enables holographic elements to be presented in the real world, here in construction
Examples of industries using AR in their work can be found in construction, such as Trimble, who enables holographic data to be presented in the real world, at the site where it is of interest.
In aeronautics, Airbus uses AR in their several of their processes.
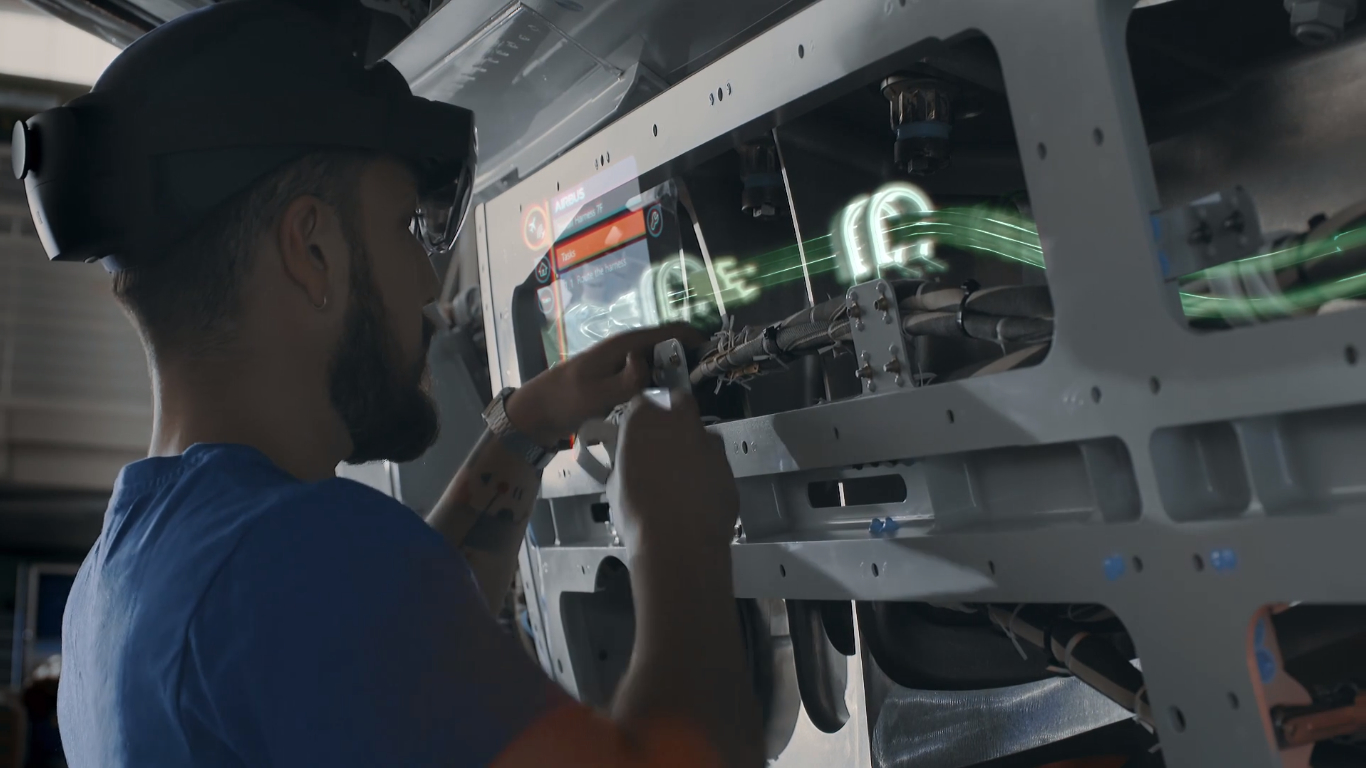 Airbus uses HoloLens for their manual assembly, amongst other purposes
Airbus uses HoloLens for their manual assembly, amongst other purposes
AR devices
Most of the industrial AR applications investigated used head-mounted displays (HMD) for their visualization and its popularity has gained the last few years. Although it could also be seen that several AR developers validated their application through more than one hardware. A similar pattern could be found in a patent analysis where 86% of the patents included HMD devices.
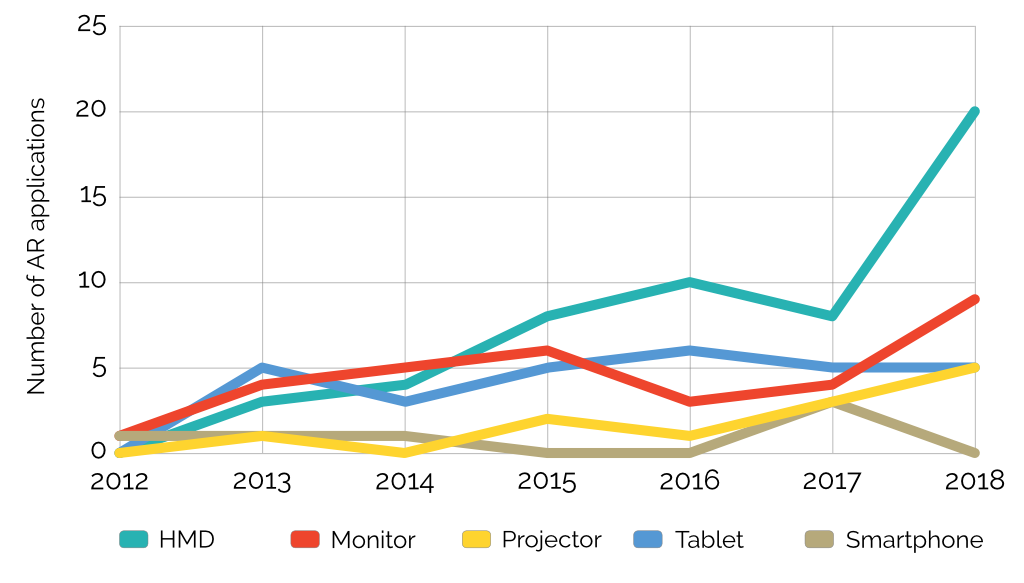 Disribution of AR applications in relation to device and year
Disribution of AR applications in relation to device and year
The researchers could see that a notable part of remote assistance solutions, where two or more users interact at the same time, has implemented different devices for processing and display technology. About 25% of all implementations investigated for the article were of this sort.
Leading benefits
90% of the analyzed articles the authors looked at converge to six main benefits, as seen below. The most announced benefit was operational time reduction along with improved production quality and increased learnability. Applications that involved human-robot interactions also reported results of user safety due to the possibility of showing the operator which locations are unsafe in real-time.
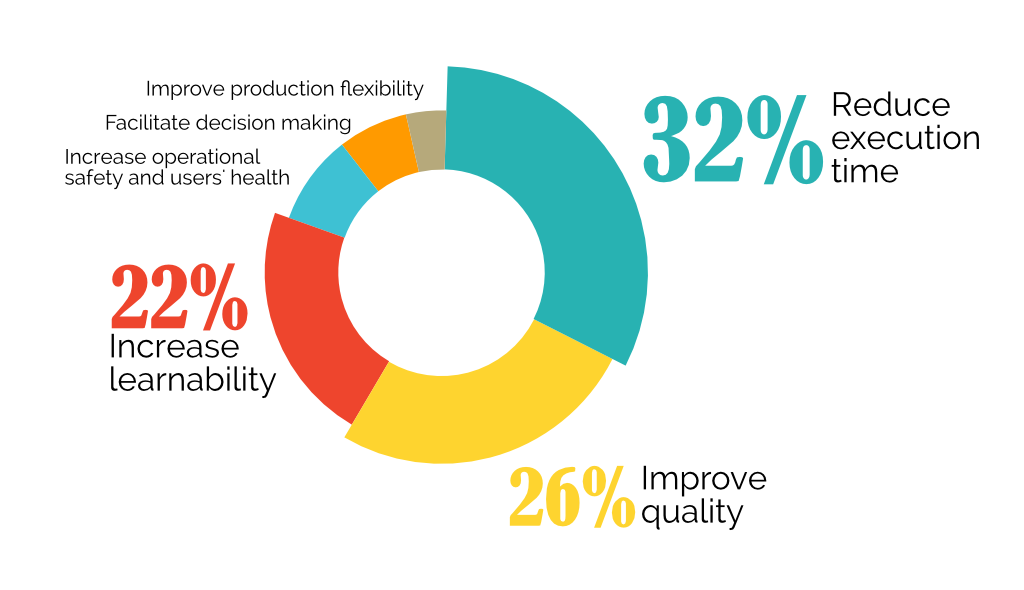 Main benefits of industrial AR applications on production environment
Main benefits of industrial AR applications on production environment
Although these benefits were found, none of the reviewed articles calculated the percentage of improvement compared to the traditional process.
Main challenges
One of the most cited difficulties was hardware limitations, which include production layout, user mobility, field of view and user interaction (mainly voice interaction problems due to noisy environments). The quality and accuracy of the virtual elements were also seen as a problem in several AR applications which is partly caused by an inaccurate tracking method as well as bad image quality and latency issues.
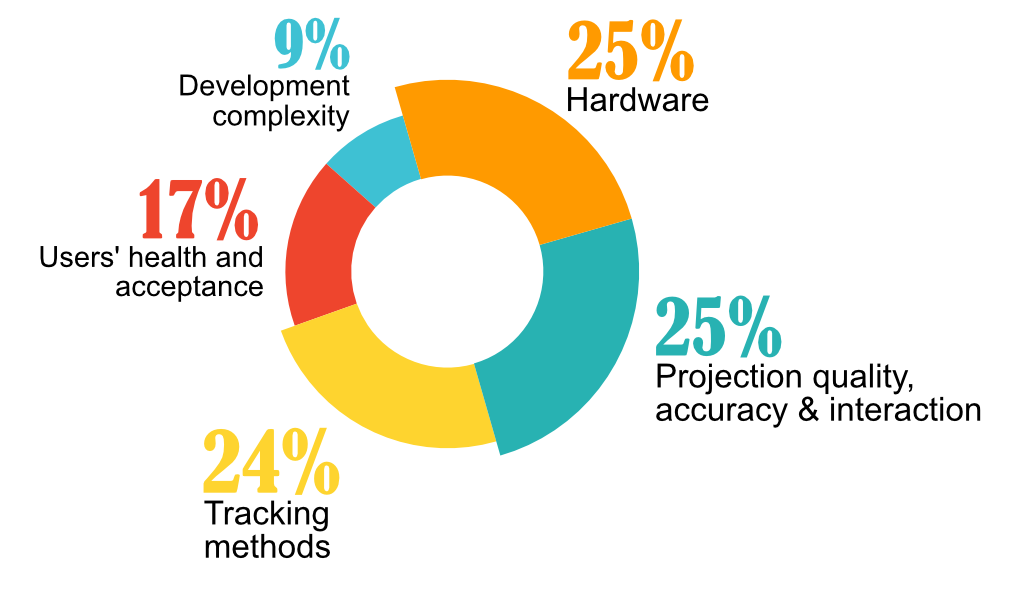 Main challenges and constraints of industrial AR applications on production environment
Main challenges and constraints of industrial AR applications on production environment
Another pain point was that industries feel that it requires deep knowledge to develop AR applications, which leads to high costs and makes it hard for companies to explore and try out the technology in search of its advantages for their specific business.
Conclusion
The interest in and experimenting with AR is increasing in many industries. Several benefits can be seen and even if the current hardware sets its limits to what is possible to develop right now there’s a lot of companies working on new and improved products.
We find it important that enterprises are willing to both implement and experiment with these new technologies to broaden the knowledge of where AR bring business value and where the limitations are, both within software and hardware. Without this knowledge, the development will be slow and several potential solutions will be delayed or even missed. AR is here, let’s be a part of shaping its future!
References:
de Souza Cardoso, L. F., Martins Queiroz Marianoa, F. C., & Zorzala, E. R. (2020). A survey of industrial augmented reality. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 139.
Photo by Spencer Davis on Unsplash
